- IP is a method by which data is sent from one computer to another over the network.Each computer which is a connected to the internet has atleast one IP address which uniquely identifies one computer from another computer.
- Internet protocol has provides each computer on a network with a unique identifier.
- The IP address is designed and controlled by Internet Assigned Number Authority(IANA).
- Internet protocol has provides each computer on a network with a unique identifier.
- The IP address is designed and controlled by Internet Assigned Number Authority(IANA).
- All computers on the Internet have unique IP addresses. As long as the IP addresses are valid, any computer can reach any other computer on the Internet with this IP address.
- A network address is an identifier for a node or network interface pf a telecommunication network.
- Network addresses are often designed to be unique across the network,although some networks allow for a local or private addresses that may not be one network.
More than one type of network addresses may be used in any one network.
There are 2 types of address
1. Physical address,example Hardware address(MAC address)
2. Logical or Software address,For example IP address.
IPv4

- Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) has been the standard IP addressing scheme since the 1980s. It’s used to get TCP/IP traffic from one computer to another computer over a network.
- An IP address is a unique address used to identify each device (i.e.computer,mobile devices,printers,etc) connected to an IP network.Internet protocol version 4(IPv4) is currently the most used addressing standard,however,IPv6 is also being used widely.
- An IP address is a unique address used to identify each device (i.e.computer,mobile devices,printers,etc) connected to an IP network.Internet protocol version 4(IPv4) is currently the most used addressing standard,however,IPv6 is also being used widely.
- An IPv4 address contains 32 binary bits.
- It has 4 octets.
- Every octet has 8 bits.
- IPv4 provides 4.3 billion IP address.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ipv4-5bdcc3d4c9e77c0051c98cca.png)




/192-168-1-0-818388_V5-5b2d1c0c43a1030036777d79.png)

- Every octet has 8 bits.
- IPv4 provides 4.3 billion IP address.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ipv4-5bdcc3d4c9e77c0051c98cca.png)
Classes on IPv4
8 bits |
8 bits |
8 bits |
8 bits |
|
Class A |
Network |
Host |
Host |
Host |
Class B |
Network |
Network |
Host |
Host |
Class C |
Network |
Network |
Network |
Host |
Class D |
Multicast |
|||
Class E |
Research |
|||
Class A
- Class A is used for large scale organizations.
- It is used for hosting.
- start from 0 to 127.
- Example - 102.126.17.226 or 10.0.10.100
Class B
- Class B is used for medium scale organizations.
- Class B from 128 to 191
- example :- 168.122.226.204 or 172.16.10.199
Class C
- Class C is used for small scale organizations.
- Class c is from 192 to 223
- example :- 200.168.212.226 or 192.168.100.100
Class D
- Class D used for Multicast.
- Class D is from 224 to 239
- Example :- 224.0.0.6 or 224.0.0.10
Class E
- Class E used for Research and Development.
- Class D is from 240 to 255
-Example:- 243.164.65.28
Division of IP address
IP addresses are divided into two types
- Network ID(Net ID)
- Host ID
The network portion is under the control of IANA and host portion in used by users.
Subnet Mask
Subnet mask is used to identify the number of bits in the network portion and the host portion in a subnet.
-In a subnet mask
- ones represent network
- Zeros represent the host
Default subnet mask
Types of IP address
1. Unicast address
- Unicast address identifies a single network interface.The IP delivers packets sen to unicast address to that specific interface.
- Example:192.168.4.1
2. Multicast address
- It is used to communicate nodes that are in a groups.
- Routing protocol used multicast address.
- Example: 224.0.0.10

3. Broadcast address
- A broadcast address is used to broadcast message to all nodes in a network.
4. Private address
- An IP address is considered private if the number falls with one of the IP address ranges reserved for private networks such as LAN.
- Private IP address are not routable over internet.
/192-168-1-0-818388_V5-5b2d1c0c43a1030036777d79.png)
5. Public address
- Public IP address are routable over internet are unique.
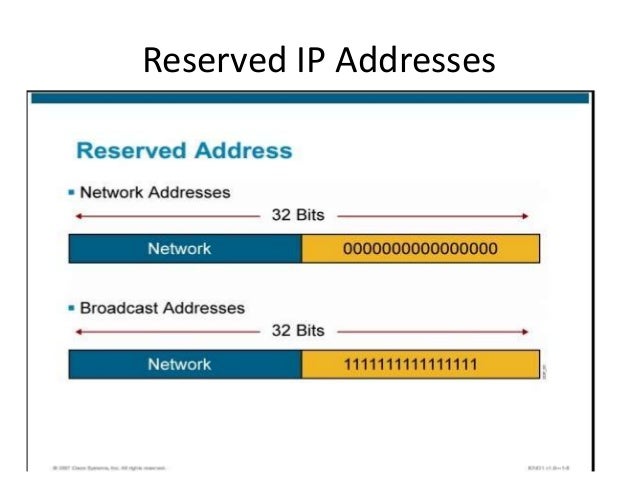
6. Reserved IP address
- Reserved IP address used for special purposes .
